Tick Diseases
Tick-borne diseases can cause a variety of symptoms. You should know what they are and how to treat them. You can learn more about the three most common tick-borne diseases in this article. Also, we’ll discuss whether or not they’re curable and whether there is a new disease that has been discovered.
What are symptoms of tick borne diseases?
Most tick-borne diseases are accompanied by a rash and fever, or flu-like symptoms. Early medical attention can help alleviate symptoms and avoid more severe illnesses with lasting consequences. Anaplasmosis and babesiosis are bacterial and parasitic diseases that are carried by ticks. These diseases affect primarily the Northeast and midwestern U.S. and require different treatments to prevent serious illness and lingering symptoms.
If you notice symptoms of a tick-borne disease, you should immediately contact a doctor. The incubation period is usually five to 14 days after the tick bite. In order to prevent the disease, antibiotics must be taken within 72 hours of the tick bite. If symptoms persist, a doctor will prescribe a longer course of antibiotics. Symptoms of untreated Lyme disease can last up to six months.
What are the three tick borne diseases?
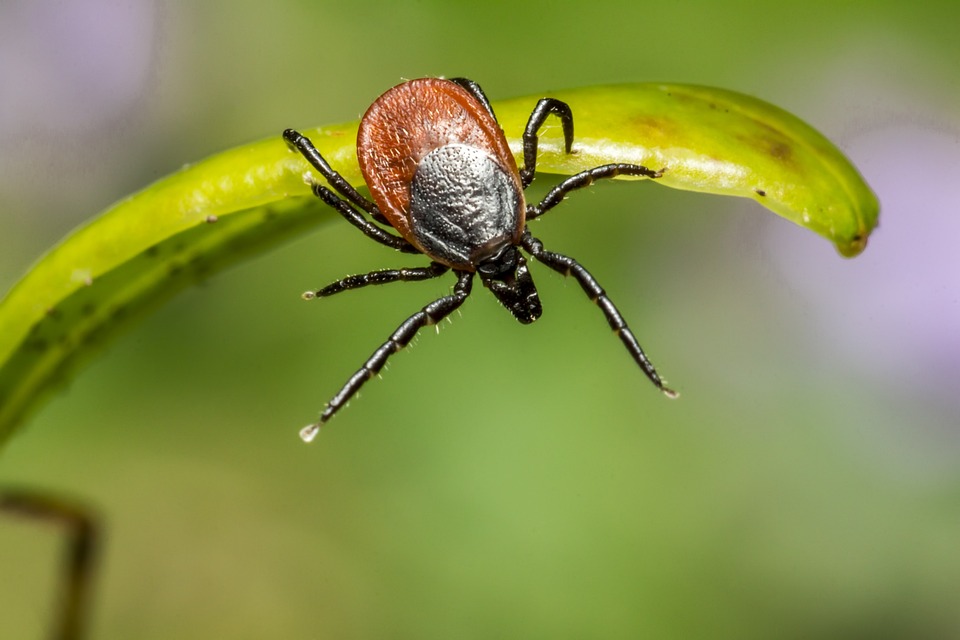
A tick’s morphology consists of two main components, the mouthparts (capitulum) and the body (idiosoma). The mouthparts of hard ticks are protruding in front of the body while the scutum on soft ticks is visible only from below. The body contains the tick’s eyes, legs, digestive and reproductive structures.
Anaplasmosis is caused by ticks. It is a contagious disease that causes a rash that can be up to three inches long. Symptoms may also include fever, muscle aches, joint pain, and fatigue. The symptoms generally appear about seven to 10 days after the tick bite.
Tularemia, also known as tick fever, is caused by the bite of a tick that carries the disease-causing bacterium tularemia. It is a potentially deadly disease, but it can be treated at home with antibiotics. Early detection and treatment are essential to minimize the risks of serious complications.
Are tick diseases curable?
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that requires antibiotics to treat. The CDC recommends taking these antibiotics within three to seven days of contracting the disease. Most people recover fully from Lyme disease after treatment. However, some people may suffer from post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome, a complication of treatment that causes persistent symptoms.
The rash caused by the tick is a characteristic reddish color. It usually starts as a small red spot near the bite site and grows larger over a few days or weeks. It may resemble a bull’s eye and can be as large as the size of a dime. The rash may spread to different parts of the body and can be debilitating. In severe cases, patients may experience paralysis of facial muscles.
There are several methods of treating tick bites. One method is to remove the tick from the skin. Ticks can attach to the skin for up to 6 hours after a tick bite. You can also wash your skin with soap and water to remove loose ticks. You can also use a skin repellent that contains DEET. However, it is important to remember that DEET doesn’t kill ticks. This is why you should use a low-DEET insect repellent, which is also safe for children. You should also avoid using DEET products on infants or people with allergies. It is also best to avoid applying insect repellents near your mouth.
What is the new tick disease?
Heartland virus is a potentially deadly disease spread by the lone star tick. It was first discovered in Missouri in 2009 and has since spread across the Midwest and Southeast. The disease is rare, but more than 50 people have been infected. Infected humans are often unable to tell they have been infected until symptoms develop.
There are several different types of tick-borne diseases. These include anaplasmosis, erhlichiosis, and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Some ticks are known to carry all of these diseases, but they tend to be more elusive than others. Other diseases caused by ticks include ehrlichiosis, tularemia, and Powassan virus.
What is the deadliest tick disease?
Tularemia, also known as rabbit fever or Pahvant Valley plague, is a deadly disease caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis. It can cause high fever, lethargy, and septicemia, and is curable with the use of antibiotics.
It is transmitted from one person to another through a tick bite. While it is the most common tick-borne disease in the Northern Hemisphere, it can also be transmitted to pets. In severe cases, this disease can cause serious long-term health problems, including heart disease, joint pain, and fatigue. Treatment is generally available only after it becomes apparent that you are infected.
In some cases, the only effective treatment is getting the affected person to the doctor immediately. The disease can lead to death in approximately fifteen percent of cases. About half of those who survive the illness may have health problems for the rest of their lives.