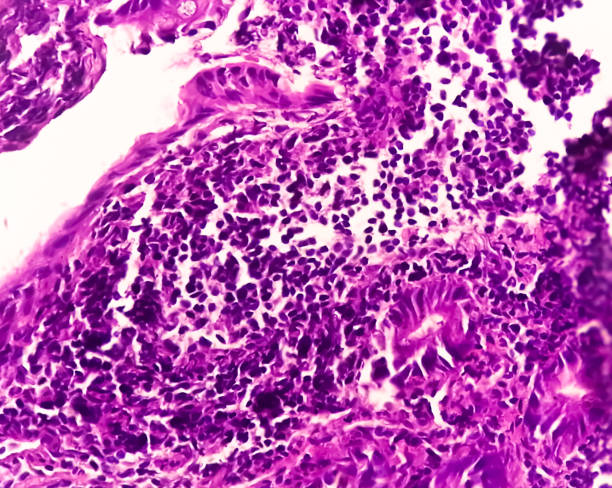
Genetic Testing For Celiac Disease
Genetic testing is useful in evaluating the possibility of celiac disease. The focus of this type of testing is on the HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8 alleles. If you have these two gene variants, your doctor may be able to confirm the diagnosis.
What color is celiac stool?
Those suffering from celiac disease may be concerned about their stool. While the occasional change is nothing to worry about, persistent changes should prompt a visit to the doctor. The color of a person’s stool can indicate several different medical problems, including malabsorption. For instance, if their stool is orange, it is likely to be caused by a deficiency in bile salts. A person suffering from celiac disease may also have unusually large amounts of fat in their stools, which makes them hard to flush out.
Normally, a person’s stool is brown or light yellow. If this color changes to any other color, it could indicate a biliary blockage, such as a gallstone or tumor. A pancreatic duct obstruction is another possible cause.
What triggers celiac disease later in life?
Genetics and environmental factors are both major risk factors for celiac disease. The disease is commonly passed down through families. If you have a family member with the disease, you have a 1 in 10 chance of getting it yourself. Stress is another major risk factor. People who are genetically susceptible to the disease should avoid gluten-containing foods. This includes bread, pasta, pizza, and other foods made from grains.
While gluten-free diets can help reduce symptoms of celiac disease, they are not a cure for the disease. Celiac disease is caused by damage to the small intestine. When the small intestine is damaged, the body cannot properly absorb nutrients. This results in nutritional deficiency and malnutrition. The lack of essential nutrients like calcium and phosphorus can cause serious problems, including bone loss, decreased immunity, and even anemia.
Can you gain weight with celiac disease?
One of the biggest questions celiac patients often ask is, “Can you gain weight with celiac disease?” It’s not impossible to gain weight while living with celiac disease. In fact, many people with the disease gain weight as a result of their disease. This is not surprising because gluten is widely present in many products, and the tiniest amount can cause bloating and weight gain.
The answer to the question “Can you gain weight with celiac disease?” is complicated. In fact, there are different types of patients with the disease, and they can have normal, underweight, or even obese bodies. The truth is that it depends. The symptoms of celiac disease can be so severe, though, that many people with the disease experience severe gastrointestinal problems. Symptoms of celiac disease can last for weeks or even months.
Where is celiac pain located?
People with celiac disease may experience pain in the stomach. This pain is caused by damage to the small intestine, which absorbs nutrients from the food. This causes a lack of vitamins and minerals. In addition, eating certain foods may cause bloating and gas. This condition is usually harmless, but it can make a person extremely uncomfortable.
Other symptoms of celiac disease include cramps after meals, and a feeling of distention that is often relieved by passing gas. Patients may also experience tingling in their feet or hands. Another common symptom is headaches, including migraines. People with the condition may also have whitish sores on their cheeks and tongue.
What happens if you ignore celiac disease?
Celiac disease is one of the most common autoimmune gastrointestinal disorders. It can be difficult to diagnose because the symptoms often resemble other digestive problems. However, a proper diagnosis can be achieved only by eliminating gluten from your diet. The best treatment for celiac disease is to stay gluten-free for life. This means avoiding any type of cereal flour. For best results, talk to your doctor about a gluten-free diet.
If left untreated, celiac disease can cause severe malabsorption of nutrients. The result is a lack of vitamins and minerals in the blood. This can cause serious symptoms like anemia, anorexia, and even diarrhea. In rare cases, untreated celiac disease can lead to a serious skin disease called Ulcerative Jejunitis (DH). It causes a blistering, burning rash on the skin and can affect quality of life.