What You Should Know About Raynaud’s Disease Gloves
Do Silver Gloves work for Raynaud’s?
Silver gloves can help those with Raynaud’s disease. The silver in these gloves can help reduce the loss of heat and numbness by reflecting 95% of the heat from the hand back to the body. In addition to this, they also reduce the amount of perspiration. However, these gloves are not a cure for Raynaud’s disease and are not a replacement for medical treatment.
Silver gloves, which are made from 8% natural silver thread, are soft, breathable and conform to the hand. They also improve microcirculation in the hands and promote injury healing. They can also reduce the appearance of fissures, blisters, and spasms.
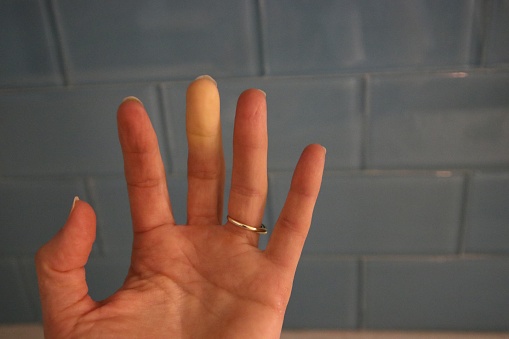
Raynaud’s disease is a disorder of the blood vessels that causes symptoms like numbness and tingling in the extremities. These symptoms are the result of decreased blood flow to the affected areas and a lack of oxygen. They can occur in any part of the body and can be triggered by stress, certain medications, and even the cold.
What is the best treatment for Raynaud’s?
Several treatments have been developed to help patients with Raynaud’s disease. Although the FDA has not approved any specific drugs to treat this condition, providers often prescribe medications approved for other conditions. These treatments can help people with both primary and secondary Raynaud’s disease.
Medications and lifestyle changes can help alleviate the symptoms. It is also recommended to avoid stressful situations and fast temperature changes. If these strategies don’t work, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics or surgery. In severe cases, a doctor may recommend removing the affected finger or toe.
The first step in treatment is identifying the underlying cause. If the underlying cause is undiagnosed, a physician will perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms. They will likely do a cold challenge test, which involves exposing the fingers to a cold temperature. The healthcare provider will also examine the tiny blood vessels in the fingernails using a microscope. If the disease is caused by a secondary condition, blood tests may be needed to rule out that condition.
In some rare cases, a doctor may prescribe a botox injection. This medication can block the nerves that cause blood vessels to constrict. However, this is an extremely rare treatment for Raynaud’s. Most doctors will try alternative treatments first. In many cases, lifestyle changes can help patients cope with the condition.
What should you avoid with Raynaud’s disease?
When you have Raynaud’s disease, you should wear gloves to protect your hands from the cold. You should also avoid stressful situations. Cold temperatures can cause skin ulcers, which can lead to more serious conditions such as gangrene. Your doctor can prescribe medication to help treat the condition. You can also purchase gloves specifically made for people with Raynaud’s disease.
The symptoms of Raynaud’s disease include numbness, pain, and tingling in the fingers, toes, and toes. In severe cases, gangrene or tissue death can occur. Although the disease is largely seasonal, it can occur even in milder climates. It is essential to understand the symptoms of Raynaud’s disease to avoid complications.
Although there’s no single test for determining whether you have Raynaud’s disease, your physician may order blood tests to rule out other illnesses. During these tests, your physician may look for abnormalities in your arteries. If you have abnormal blood vessels, this may be a sign of another disease such as scleroderma.
What foods to avoid if you have Raynaud’s?
A healthy diet is essential to preventing and treating Raynaud’s disease. It may even help you feel better. Although there are no known cures for Raynaud’s, some supplements, such as ginkgo biloba, have proven to be beneficial to patients with the disease. However, if your symptoms are severe or recurring, it is important to seek medical help immediately.
There are two types of Raynaud’s disease: primary and secondary. The first type occurs in adults without any underlying disease, while the latter develops in adults of any age. However, secondary Raynaud’s is more serious and may result in tissue death or ulcers.
Your doctor can determine if you have primary or secondary Raynaud’s disease. After reviewing your symptoms, your doctor may decide to do a physical exam and run blood tests. Your doctor may also want to check the health of the blood vessels in your fingernails to rule out other conditions that cause your symptoms. If you do have Raynaud’s disease, you should avoid extreme temperature changes. If you must go outside, wear warm clothes.
What deficiency causes Raynaud’s?
There is no cure for Raynaud’s disease, and treatments are usually focused on preventing or treating the underlying cause of the disease. However, there are certain measures that you can take to manage your symptoms, including avoiding cold temperatures and wearing gloves.
Some of the causes of Raynaud’s disease are unknown, but one factor has attracted extensive study: nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is produced in the body by a gene called nitric oxide synthase. In people with primary Raynaud’s disease, the gene encoding NOS is overexpressed while those with secondary cases have an underexpressed version.
The cause of secondary Raynaud’s disease is not yet known, but it is believed that certain autoimmune diseases may cause the condition. It is important to note that 1 in 10 people with primary Raynaud’s develop secondary forms of the disease. The best way to determine whether your case is caused by secondary or primary Raynaud’s is to consult with a physician.
What is the root cause of Raynaud’s syndrome?
This condition, which affects the fingers and toes, is caused by a lack of blood flow to these parts. The most common trigger is exposure to cold temperatures. However, emotional stress and cigarette smoking can also trigger the condition. Although there is no known cure for this condition, it can be managed through simple lifestyle changes, such as wearing warm clothing or quitting smoking.
Certain medications can cause secondary Raynaud’s. These include beta blockers, migraine medications, chemotherapy drugs, and some over-the-counter cold medications. Additionally, exposure to certain chemicals can trigger episodes. Finally, people with family history of the condition have a higher risk of developing it.
Raynaud’s is a condition in which the blood flow to the fingers and toes becomes diminished. The affected area may also experience changes in color and tingling. It is often painful and can lead to ulcers or tissue death.
Does Raynaud’s qualify for disability?
Raynaud’s disease can be a serious issue, affecting a person’s ability to walk and do daily activities. The symptoms are often painful and bothersome, limiting a person’s ability to perform everyday tasks. In addition to pain, Raynaud’s disease can lead to ulcers and serious infections as a result of poor circulation. Because of these problems, people with Raynaud’s disease may be eligible for disability benefits.
To qualify for disability benefits, Raynaud’s disease applicants must prove their inability to work and must show how their condition affects their lives. The Social Security Administration evaluates the severity of the symptoms and the side-effects. Various types of evidence will be used during the process. These may include medical records and paperwork from treating providers.
The symptoms of Raynaud’s disease can include coldness and numbness, and the color of the skin can change. The disease is more common in women than in men, and people who live in colder climates are more likely to develop it. In addition, people who use vibrating tools may suffer from Raynaud’s.