Parathyroid Disease Symptoms
Parathyroid disease symptoms often are not apparent in the early stages. They differ from person to person depending on the type of the disease. Listed below are some common signs and symptoms of parathyroid disease and how to treat them. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should see your doctor to determine the cause of the problem.
What are the symptoms of parathyroid disease?
If you are experiencing symptoms such as high blood calcium levels, osteoporosis, and other bone problems, you may have parathyroid disease. Your doctor may prescribe vitamin D to treat your condition or perform surgery to remove your parathyroid glands. However, you must be aware of the risks involved in surgery.
One of the biggest risks of hyperparathyroidism is heart problems. In fact, over half of patients with this condition have experienced heart problems. Some symptoms of heart problems include palpitations and racing heart. Beta blockers can help treat these heart problems. You should also be aware of the symptoms of depression.
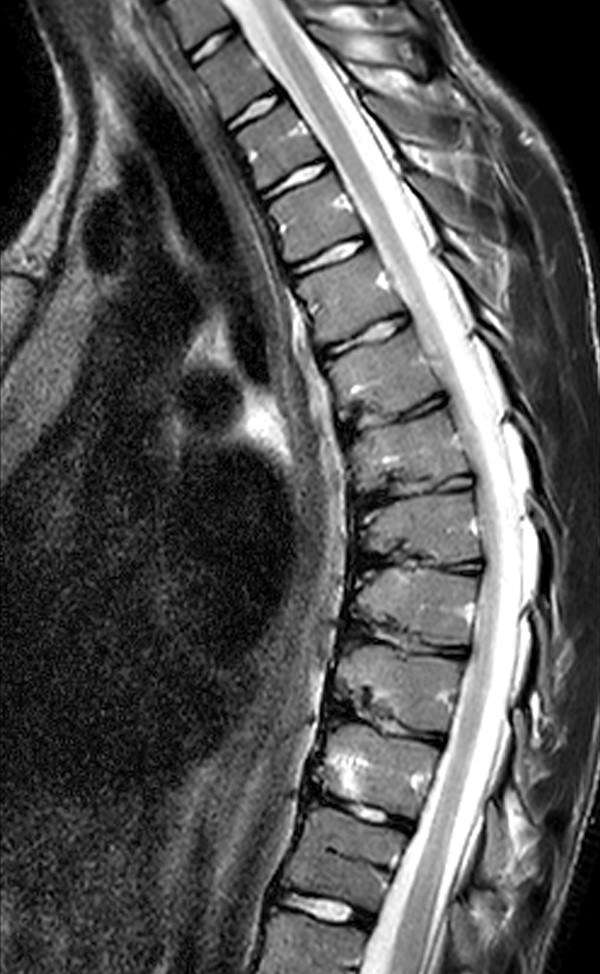
Your doctor will review your medical history and conduct a physical exam. He may also order blood tests, urine tests, and imaging tests. These tests may include a CT scan, MRI, ultrasound, and x-ray. Sestamibi scanning is another test that may be performed. This type of scan uses a radioactive chemical that will appear on a special camera.
What is parathyroid disease caused from?
The parathyroid gland is a distinct organ in the body that produces the hormone PTH. The body needs this hormone to regulate calcium levels in the blood. When the gland is overactive, it pulls calcium out of the bones, resulting in hyperparathyroidism or parathyroid disease.
Hyperparathyroidism is the most common type of parathyroid disease. This condition is caused when one or two parathyroid glands become overactive. These overactive glands produce too much PTH, causing too much calcium in the blood. In some cases, hyperparathyroidism can also be caused by a benign tumor on the parathyroid gland. Other causes of hyperparathyroidism are radiation therapy and hereditary hyperparathyroidism.
The parathyroid glands are pea-sized organs located near the thyroid gland. These glands make parathyroid hormone, which is necessary to maintain the normal balance of calcium and phosphorous in the blood. When the glands become overactive, the body produces excess amounts of this hormone, which leads to hyperparathyroidism. The problem can also be the result of an enlarged parathyroid gland, which is an uncommon cause of hyperparathyroidism.
What is the most common parathyroid disease?
If left untreated, parathyroid disease can lead to a stroke and kidney stones. But there is a good news: a simple 17-minute procedure can fix this problem. Usually, patients go home with a Band-Aid on their neck. But there are other symptoms of parathyroid disease that you should be aware of.
One of these is hyperparathyroidism, a condition in which parathyroid glands make too much PTH. This condition affects the body’s ability to absorb calcium and phosphorus. PTH helps regulate calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood, and it plays an important role in bone health.
If you’ve been diagnosed with this disease, you should consult with your doctor as soon as possible. Generally, a doctor will give you a treatment plan based on the specific symptoms that you’re experiencing. In some cases, surgery may be necessary.
How do you treat parathyroid disease?
Parathyroid disease is a serious condition that can have devastating effects on a person’s health. If left untreated, it can cause fatigue, kidney stones, and stroke. It can also cause a person to lose weight and feel thirsty more frequently than usual. Luckily, the treatment of this disease is simple. Doctors perform a mini-operation to remove a diseased parathyroid, and the patient can go home the same day.
The first step is to get a diagnosis. A blood test can help your doctor identify the disease. It also allows him to determine the severity of the condition. Blood tests can reveal whether parathyroid hormone levels are too low, or if there are other underlying causes. Other tests may include a kidney ultrasound or an ultrasound scan of the neck. Once your doctor has confirmed the diagnosis, treatment options can include monitoring and surgery. In some cases, surgery will be necessary to remove the diseased parathyroid glands. This surgery can be performed minimally invasively or as a standard neck exploration.
Can you live a long life with parathyroid disease?
The prognosis for parathyroid disease is uncertain, and it varies widely between patients. It is based on several factors, including the patient’s medical history, the stage of the disease, the type of treatment, and survival statistics. Fortunately, new treatments and methods are being tested.
Treatments for parathyroid disease can include surgery to remove the overactive parathyroid. The surgery can help to control calcium levels in the blood. In most cases, patients can expect to improve after the surgery. If left untreated, the disease may eventually lead to kidney stones, osteoporosis, and a poor memory.
Parathyroid glands are made up of 80,000 tiny cells that measure calcium levels in the blood. They produce parathyroid hormone, which helps your body to absorb calcium. This hormone is secreted by the gland and is released into the bloodstream. The gland turns on and off hundreds of times a day, and it acts independently of other cells. In some cases, the growth of the parathyroid gland cell may be so slow that it goes undetected for years.