Leptomeningeal Disease
There are many questions surrounding leptomeningeal disease, including: How common is it? Can it be fatal? What are the symptoms and causes of death? And, does leptomeningeal disease go away on its own? Read on to learn more about this common type of cancer.
Can you survive leptomeningeal disease?
There is no specific cure for leptomeningeal disease, but there are treatments available that can improve your outlook. The most common treatments are chemotherapy and radiation. But intrathecal chemotherapeutics have improved the median survival rate. It is important to get treatment early to avoid complications.
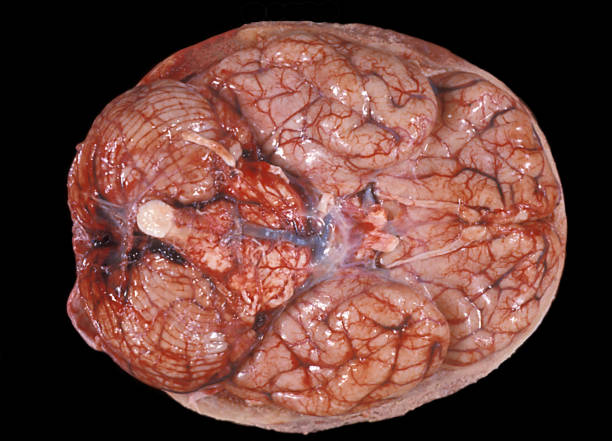
Leptomeningeal disease is a complication of cancer that spreads to the central nervous system. Most cases involve the brain, but a growing number also involve the leptomeninges. This form of cancer metastasis, which occurs when cancer cells infiltrate the leptomeninges, has a poor prognosis. Patients usually die within a few weeks, but it is possible to live longer with effective treatments.
The symptoms of this disease include a headache, nausea, and vomiting. It may also cause weakness in the legs and a weakened heart. Treatment can be expensive, but it can make the disease less severe and can help you recover from its symptoms. The prognosis for leptomeningeal disease is 6 months if you combine treatments with radiation and khimiotherapy.
What causes death in leptomeningeal disease?
Leptomeningeal disease is a type of cancer that can spread throughout the leptomeninges or cerebrospinal fluid. It is an uncommon form of cancer, but is becoming increasingly common as healthcare providers encounter more people with this disease. It is difficult to treat and is often a terminal disease, but there are treatments available to help patients manage the symptoms and maintain their quality of life.
Radiation therapy is one method used to treat leptomeningeal disease. This treatment is aimed at reducing edema and inflammation of the nervous system. This treatment can also be used to treat patients with leptomeningeal metastases. Glucocorticoids are sometimes used to reduce the pain of patients suffering from leptomeningeal metastases.
How common is leptomeningeal cancer?
Leptomeningeal cancer is rare but incurable, and there are treatments to help alleviate the symptoms. Treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. In addition, some tumors respond well to oral chemotherapy. Treatments also include immunotherapy. Leptomeningeal cancer is a disease that can occur in the brain, spinal cord, or meninges.
The prognosis of leptomeningeal cancer depends on many factors, including the extent of the cancer and its response to treatment. While a person with leptomeningeal cancer usually has a short life expectancy, there are some people who respond to treatment very well. With new treatment options able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, the survival rate is expected to increase.
The symptoms of leptomeningeal cancer can be very similar to those of cancers of the brain, including facial weakness, double vision, and difficulty swallowing. However, symptoms of leptomeningeal disease may not be apparent until the cancer has spread to other parts of the brain. Treatment for leptomeningeal cancer depends on the stage of the disease, the extent of the metastases, and the person’s overall health.
Can leptomeningeal go away?
A leptomeningeal metastasis is a type of cancer that has spread to the meninges or cerebrospinal fluid. These layers of tissue protect the brain and spinal cord. Cancer cells can reach the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid through the spinal canal.
People who suffer from this disease may experience neurological symptoms like facial muscle weakness and difficulty swallowing. It can also affect their ability to think clearly. It is increasing in incidence as people are living longer. Healthcare providers use MRIs to diagnose the condition. Treatment may improve neurological function and ease symptoms.
As the number of patients with leptomeningeal metastases increases, the treatment for these tumors is becoming more advanced and more sophisticated. Patients should be evaluated by a specialized neuro-oncological tumour board to ensure they are receiving the best care possible. As a side effect of cancer therapies, leptomeningeal metastasis can lead to more severe complications, such as stroke.
Can a CT scan detect leptomeningeal?
Although CT scans are not a reliable method to diagnose leptomeningeal disease, they can be informative in certain situations. For example, they may show an increase in protein levels, or a decrease in them. If the protein levels are high, this could mean a blockage or inflammation. High pressure and pleocytosis in the CSF are other common findings. Glucose levels are usually reduced as well. In fewer than five percent of patients, the CSF profile is normal.
Although leptomeningeal disease may be difficult to diagnose, the recent advances in cancer treatments promise more treatment options for this disease. However, the most common symptoms are headaches, double vision, and nausea. Leptomeningeal disease can also cause problems with walking and urinary control.