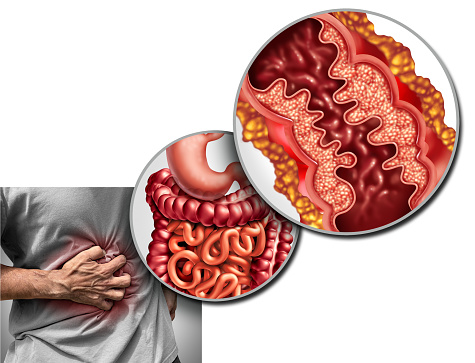
Is Crohn’s Disease Contagious?
If you’re wondering if Crohn’s disease is contagious, you’re not alone. Over one in three people have the condition. Many of these people also have anemia, so you may want to get your blood tested to rule out other illnesses. Your doctor may also want to perform a stool test to check for parasites and bacteria. In addition, you’ll need to have a colonoscopy, which involves looking inside your colon with a camera and endoscope. These tests will also show if there is inflammation.
Inflammatory bowel disease
The causes of Crohn’s disease and inflammation bowel diseases are still unknown, but some researchers believe they may be triggered by a virus or bacterium. In any case, the disease is characterized by an abnormal immune response, which attacks healthy tissues in the digestive tract. In addition to genetics, environmental factors, and the microbiome are considered possible triggers.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic inflammatory disease of the lining of the colon. It is caused by the body’s immune response to certain environmental triggers. Genetics also plays a role in the development of the disease, as people with a family history are more likely to have an inappropriate immune response. A doctor can treat inflammatory bowel disease with surgeries, which may remove damaged sections of the gastrointestinal tract.
Inflammatory bowel disease is not contagious. However, the symptoms of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are similar. Patients may feel abdominal pain or bloating, but Crohn’s disease may involve more severe symptoms. Some people may even suffer from vomiting and diarrhea.
Despite what many people believe, Crohn’s disease and inflammation bowel diseases are not contagious. However, there is no direct evidence that Crohn’s is contagious. Researchers suggest that environmental factors, genetics, and immunologic factors play an important role in the development of the disease. Dietary changes and stress are also believed to contribute to the development of the disease.
Anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce the inflammation. Azulfidine, olsalazine, and mesalamine may be helpful. Metronidazole, a type of antibiotic, may also help. These antibiotics help kill germs that cause diarrhea and other symptoms.
The MAP theory, which supports that Crohn’s disease is contagious, is based on the findings of research in a group of seven people who had common diseases. The study determined that these individuals shared common environmental exposures. These individuals were likely exposed to contaminated water. As a result, the researchers suspected that the contaminated water they used in their homes had the bacteria that led to the development of Crohn’s disease. However, it is important to note that many individuals who have MAP are not affected with Crohn’s disease.
Although the disease is contagious, it can be treated. Surgery can be performed on people with Crohn’s disease. This procedure can help the patient return to a normal life. However, Crohn’s disease is not completely cured after surgery, and most people will need to take medicines to manage the symptoms. However, the recovery rate after surgery is high – 85 to 90 percent of patients will have no symptoms a year after surgery. And up to 20 percent of patients will not experience any symptoms for 15 years after surgery.
The likelihood of developing Crohn’s disease is highly dependent on one’s genetic makeup, age, and environment. Most people with IBD develop the disease before the age of 30, although some people develop the disease in their 50s or 60s. The disease is more common among white people, but is becoming more common among people of other races. It is also more difficult to diagnose in children and adolescents because the symptoms are often dismissed.
Although it’s difficult to diagnose inflammatory bowel disease, there are treatments available. During flare-ups, inflammation in the digestive system can result in diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. Dietary changes can help reduce the symptoms, and some people may even be able to go back to normal lives without medication.
People who have Crohn’s disease and inflammation bowel diseases may also have an increased risk of colon cancer. As a result, patients with this condition should undergo a colonoscopy at least every 8 to 10 years, starting at age 45. This is because the longer the disease lasts, the higher the risk of developing colon cancer.
Fistulas
Fistulas are narrow passages that can develop due to inflammation in the digestive tract. These abnormal tracts can connect organs and external surfaces. Anal fistulas connect the anal canal to the skin, and vaginal fistulas connect the bladder and rectum. In some cases, the fistula may even form an abscess.
Surgery is one of the treatment options for fistulas. The procedure involves inserting a thin surgical cord to drain the infection and allow the fistula to heal. This procedure is done over several weeks and may be combined with anti-TNF therapy to reduce the risk of infection. Patients may feel some discomfort after the surgery, but pain pills are generally not necessary.
Fistulas are more common in children than in adults. For this reason, it’s important to choose your doctor wisely. You should feel comfortable with him or her, and he or she should listen to your concerns and desires. If your doctor is not listening, you may want to switch doctors. There are more treatments available than ever before, and a new doctor may be able to help you.
Studies in adults with Crohn’s disease have shown that the disease can be associated with fistulas. In fact, fistulas and cancer in women with Crohn’s disease are associated. A study published in Der Chirurg in 1987 suggested a connection between the two conditions.
Inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn’s disease, are often difficult to treat. While conventional treatment approaches may work for some patients, fistulas are a real challenge. One promising treatment option is cell therapy. Stem cells have shown promising results in several inflammatory diseases.
Current medical treatments for perianal fistulas in patients with CD include antibiotics, immunomodulators, and biologic agents. However, perianal fistulas still remain a challenge. Fortunately, new biologic agents and surgical techniques have changed the treatment paradigm.
A perianal fistula is a common complication of Crohn’s disease. It is associated with severe symptoms. In severe cases, it can lead to the development of a stoma or proctectomy. In the past, complete fistulectomy was the standard treatment for this condition.
A fistula forms when the intestinal wall is inflamed. Sometimes it is caused by an abscess or ulcer. These lesions leak acidic gastric fluids. These lesions can grow until they connect to other organs. There are several types of fistulas and signs and symptoms of each vary from person to person. If you suspect a fistula, see your healthcare provider immediately.
Fistula treatment methods have changed substantially in the past two decades. Once the only treatment option was surgical repair, now there are various more conservative approaches, including medical therapy and surgery. While medical therapy does have its drawbacks, it is generally a safe and effective treatment for internal fistulas. The downsides of surgery include discomfort, cost, and a higher risk of complications.
Fistulas are associated with significant morbidity in people with Crohn’s disease and may affect their quality of life. As a result, treatment has become more multidisciplinary, including collaboration between gastroenterologists, colorectal surgeons, and endoscopists. Additionally, new biologics and cell-based therapies have been developed. In addition, the treatment of a fistula in a patient with Crohn’s disease has improved significantly.
Infliximab has been approved as an effective treatment for the treatment of fistulas in people with Crohn’s disease. Infliximab is a corticosteroid sparing agent but is often toxic. Because of this, it is important to consider when and how to administer the drug. Infliximab is best administered to patients with chronic disease who have already undergone immunosuppressive treatment.
Stem cell infusion has the potential to treat a wide range of human disorders. Infusing stem cells may be an effective treatment option for fistulas caused by Crohn’s disease. While this treatment remains experimental, a growing number of scientists are studying the benefits of this procedure.