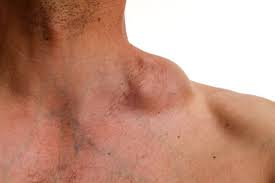
Hodgkins Disease
Hodgkins disease is a type of cancer that begins in the lymph nodes of the body. Some lymph nodes are located in more visible places, such as the chest cavity, but the disease can spread to virtually any part of the body. There are several symptoms associated with Hodgkins disease.
Is Hodgkin’s disease curable?
The good news is that Hodgkin’s disease is curably curable, even in its advanced stages. Treatment is usually a combination of chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The treatment plan chosen by the patient and the healthcare provider depends on the stage of the disease, the patient’s preferences, and any risk factors. In some cases, a bone marrow transplant may be required.
Almost 80% of patients with Hodgkin’s disease are cured after standard chemotherapeutic regimens. However, a small proportion will require salvage treatment. This is why the treatment cost for the first, second, and third lines of chemotherapy are analyzed. To compare the costs of each treatment regimen, the patients were grouped into three groups: first-line cures, patients who did not respond to first-line therapy, and patients who had received one or two consecutive treatment regimens but did not respond.
Is Hodgkin’s disease fatal?
Hodgkin lymphoma is a relatively aggressive cancer that can spread throughout the body. Fortunately, it is one of the most treatable types of cancer. Treatment will vary depending on the stage of the disease and the patient’s age and health. Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment, and is followed by radiotherapy. Surgery is rarely used.
The exact cause of Hodgkin’s disease is unknown, but there are several risk factors. Individuals with a weakened immune system are at an increased risk. People with Epstein-Barr virus may also have a higher risk.
What is an early symptom of Hodgkin’s disease?
Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a type of cancer in the lymphatic system. It can also occur in other organs, including the liver and bone marrow. Several tests can help doctors identify the type of cancer and decide what course of treatment is best. Treatment usually consists of chemotherapy and radiation therapy. In severe cases, bone marrow transplants may be required.
Diagnosis is usually made after a comprehensive patient history and clinical evaluation. A detailed examination can reveal characteristic findings, such as lymph node swelling. A biopsy can confirm a diagnosis, especially if the disease is in the lymph nodes. The lymph node tissue is then examined microscopically to determine whether it contains Reed-Sternberg cells.
What causes Hodgkin’s disease?
Hodgkin’s disease is a type of cancer that affects the lymph nodes. The nodes are located in the armpits, chest, abdomen, and groin. If left untreated, the disease can spread to other lymph nodes and the spleen. In addition, patients can experience weight loss, abnormal enlargement of the spleen, liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal system.
Hodgkin lymphoma is diagnosed by a physician after a thorough physical examination. During the examination, the physician will feel for abnormal masses on the lymph nodes. Some lymph nodes are deep in the body and may enlarge. The spleen can also become enlarged and can be felt under the left rib cage. The physician will then perform a lymph node biopsy to determine if the masses are caused by the disease.
The causes of Hodgkin’s disease are not fully understood. People with a weak immune system may be more susceptible. People who are taking drugs that suppress the immune system are also at risk.
Is Hodgkins a form of leukemia?
Hodgkins disease is a type of leukemia that attacks certain B cells in the bone marrow. It can be treated with chemotherapy, which uses drugs to kill cancer cells and stop them from multiplying. It may also be treated with radiation therapy using high-energy X-rays. Another type of treatment for Hodgkins disease is immunotherapy, which boosts the immune system. One of the most important types of immunotherapy is called a checkpoint inhibitor.
People who have Hodgkins disease may also have other forms of the disease. This type of leukemia affects the lymphatic system, which is an intricate network of vessels and nodes in the body. The lymphatic system is responsible for removing waste products and fluid from the body. White blood cells, called lymphocytes, are produced in this system. These cells help the immune system fight off various infections.