Hand Foot Mouth Disease in Adults
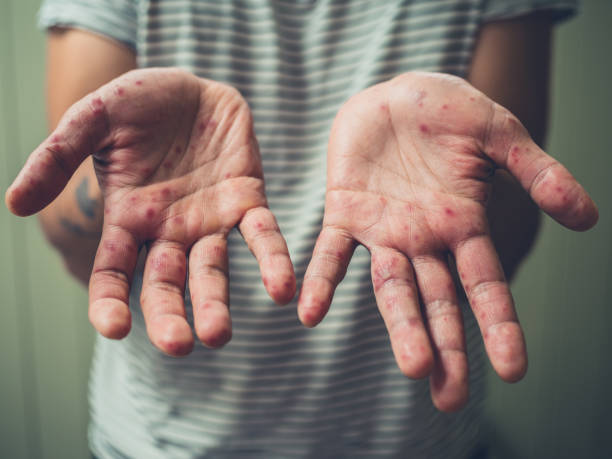
Hand foot mouth disease is an infectious rickettsial disease that primarily affects children under 10 years of age. Common symptoms include oral enanthema and a rash on the hands and feet. However, it can also develop in adults. Different clinical presentations of hand foot mouth disease make diagnosis complex. Three cases are discussed to highlight the diagnostic challenges.
Can Hand-Foot-and-mouth be serious in adults?
Hand-Foot-and-Mouth disease (HFMD) is a contagious viral infection that can affect both children and adults. It is often spread through close contact and can lead to dehydration and painful sores in the mouth and throat. Although most cases of HFMD are mild, they can still be distressing and require medical treatment.
It can also be passed to newborns, though these cases are uncommon. The disease can also affect people who work in child-care settings. For this reason, frequent hand washing is important to prevent the virus. People with HFM should avoid sharing clothing and personal hygiene items with others. Those with the disease should also wash surfaces and clothing thoroughly.
The symptoms of HFMD usually begin three to seven days after the infection. Children may have fever and sore throat, but these symptoms will go away within a week or two. If the infection is severe, the infection can spread to the brain and spinal cord.
What does hand-foot-and-mouth look like in adults?
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (HFMD) is an infectious disease caused by a number of viruses. Most people develop immunity to these viruses as they age, but it is still important to keep the disease in check. To prevent the spread of the disease, you should avoid touching infected areas, wash your hands thoroughly, and stay home from school and work until the symptoms go away. In order to prevent the infection from spreading, you should also use a clean cloth or tissue to cover your mouth when sneezing.
While hand-foot-and-mouth disease is most common in young children, it can also affect adults of all ages. The symptoms of this infectious disease include red, painful sores on the palms and soles of the hands, and blisters in the mouth. If left untreated, the disease can cause dehydration. People with severe symptoms may need to receive IV fluids at the hospital.
How contagious is hand-foot-and-mouth to adults?
Hand foot and mouth disease is caused by a virus that can spread from one person to another. You can get the disease by touching infected surfaces, but you can prevent it by washing your hands frequently. Moreover, you should disinfect frequently-touched surfaces. There is no known cure for this infection. Although antibiotics may help, they can only relieve the symptoms.
Infected people are most contagious during the first week after contracting hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD). But, the virus can stay in their bodies for weeks after they stop experiencing symptoms. This means that an infected person can still spread the virus to other people even after they’ve stopped showing symptoms. People with mild symptoms of the disease are still contagious during the infection. However, they are more contagious during the first week of the illness.
Should I go to work with hand foot mouth?
If you think you may be infected with hand, foot, and mouth disease, you may want to stay home until you’re better. Although it’s not a serious condition, it’s important to limit contact with others. You should also stay home if you have a child who has been diagnosed with the condition.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a highly contagious virus. It is easily spread through close contact, kissing, and touching fecal matter. While it is most common among children, it can also affect adults. Follow the instructions carefully to prevent spreading the infection to others.
Hand Foot mouth disease (HFMD) is a self-limiting viral illness that usually affects young children. It is caused by the coxsackievirus A16 and enterovirus 71, and is generally mild. Adults who have a normal immune system are rarely affected. However, severe cases can cause widespread pain and joint pain. If these symptoms last for more than a week, you should see a physician.
If you suspect that your child has HFM, make sure to inform the daycare or school that your child is ill. Children who are afflicted with the condition should stay home from school or daycare until the fever has passed and the blisters and mouth sores have healed completely.