Forestier’s Disease – Causes and Symptoms
This article discusses what causes Forestier’s disease and how to diagnose it. You may also be interested in finding out the symptoms and treatment of this disease. A cure is not always available. If you suspect that you have the disease, the first step is to contact a veterinarian or medical professional. There are some treatments that can help you manage the symptoms and prevent further complications.
Is there a cure for Forestier’s disease?
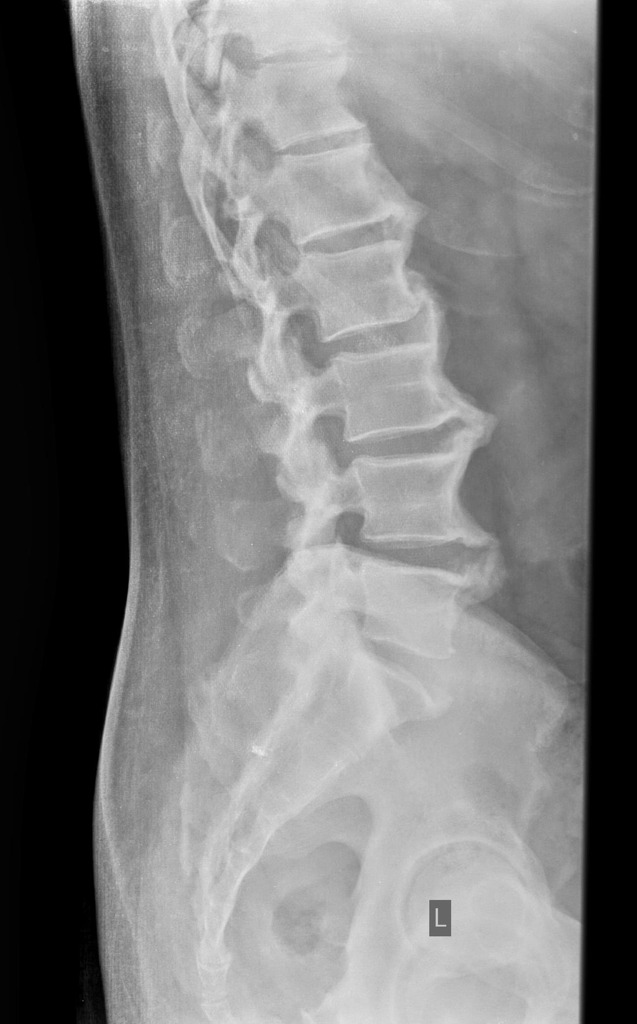
Forestier disease, also known as diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH), is a condition characterized by thickening, calcification, and ossification of soft tissues. It typically affects the thoracic and axial skeletons. This condition is related to metabolic factors that affect the formation of new bone. Unfortunately, there is no known cure for this disorder.
There is no known cure for this disorder, but there are some treatments that can relieve symptoms and even reverse the condition. Surgery may be an option in the most severe cases. Forestier’s disease is usually treated conservatively. However, in some severe cases, it can result in severe airway obstruction, which requires surgical resection of the osteophytes. In one case, a 55-year-old man with symptoms of Forestier’s disease underwent anterior cervical osteophytectomy to relieve his dysphonia.
Although there is no specific treatment for Forestier’s disease, treatment for symptoms is essential. The most common symptom is dysphagia, which is caused by a variety of mechanisms. Diagnostics for the condition are usually made by radiological studies, and treatment is initially conservative. Surgical interventions are sometimes necessary if dysphagia is refractory or if the patient cannot swallow, but they aren’t a cure for the condition.
Is there a cure for DISH disease?
Although the cause of DISH is not yet known, it is suspected to be caused by abnormal osteoblastic growth and function in the osteoligamentous binding center. However, this theory is still not universally accepted. The disorder has been linked to specific factors. For example, obesity and sedentary lifestyle are both associated with increased risk of DISH.
DISH may cause pain, stiffness, and bone spurs around the spine. These spurs can compress nerves and cause problems for the patient. Other symptoms can include difficulty swallowing or numbness or tingling in the legs and arms. However, many people with DISH show no symptoms and are not diagnosed until a doctor performs an imaging test.
DISH is typically treated with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as acetaminophen. In severe cases, a doctor may recommend local corticosteroid injections. Physical therapy can also help decrease stiffness and increase range of motion. In some cases, surgery is necessary to remove bone spurs and relieve pressure on the spinal cord. Regular aerobic exercise can also improve endurance and keep the body nimble, which can help patients cope with DISH.
How is Forestier’s disease diagnosed?
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis, also known as Forestier’s disease, is a degenerative disorder of the skeletal system. It causes stiffness and pain in the neck and upper back, and can also affect the knees and elbows. The underlying cause is unclear, but it can result in serious complications. Symptoms vary from person to person.
Forestier’s disease is not uncommon in the elderly, but it is often misdiagnosed and goes untreated. Because the symptoms can be quite similar to those of other pharyngeal disorders, radiography of the cervical spine is an essential diagnostic tool. Early diagnosis is crucial for multidisciplinary management and improves patient outcomes.
In patients with osteophytes, a bone scan may reveal a degenerative process that is causing exuberant bone formation. The disease is usually cured without surgery, but surgical resection is an effective treatment in severe cases.
How serious is DISH disease?
The symptoms of DISH disease can vary depending on the location of the symptoms and the extent of spinal deformity. The disease can cause pain and loss of feeling and can lead to paralysis. The doctor will look at the range of motion and any tenderness around the spine to make a correct diagnosis.
The most common imaging test used to diagnose DISH is a thoracic spine radiograph. This is performed on patients who have primary or diffuse symptoms. The radiograph helps determine the exact location of the affected vertebra. Imaging tests will also help identify if there is any extra bone growth in the vertebral column. The extra bone growth must involve at least three adjacent vertebrae. In addition, the spine should be evaluated for calcification. This calcification can appear as a candle wax oozing down the spine.
Non-surgical treatment is the preferred method for treating DISH. Treatment may involve the use of medications such as analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and muscle relaxants. In some cases, surgery is necessary. However, surgery is only used if the bone spurs are causing pressure on the spine or nerve root. In such cases, bone spurs can be removed to reduce pain and ease symptoms of DISH.
What does DISH feel like?
DISH, or degenerative spine arthropathy, is a type of arthritis that can affect the tendons and joints of the lower back, neck, and shoulders. In patients with this condition, the ligaments become stiff and can cause abnormal bone growth. Bone spurs can also form where the ligaments connect to the bones. The condition can be accompanied by a decreased range of motion and persistent back pain. Symptoms are typically most noticeable in the morning and can worsen over time.
DISH is rare before age 40, but it becomes more common as people age. It’s also more common in men than in women. If left untreated, DISH can lead to a stiff spine and less flexibility. The calcified ligaments may also press against other nearby structures, such as the oesophagus, which can result in difficulty swallowing.
DISH can be difficult to diagnose as it’s often asymptomatic. However, a physical exam will reveal that you have the disorder if you experience pain, stiffness, or decreased mobility in one or more joints. DISH typically affects the thoracic spine on the right side, but it can affect other parts of the body.
Does DISH affect your heart?
Researchers have shown that high levels of CRP are associated with increased CV risk. However, the association was not statistically significant. Moreover, higher CRP levels are associated with a greater BMI, particularly in females. Other findings show an increased risk of coronary artery calcifications in DISH patients, even after adjusting for age.
A physical therapist can help you improve your range of motion and reduce the stiffness associated with DISH. He or she can provide you with guidance and exercises. In more serious cases, surgery may be necessary to remove bone spurs from the spine and relieve pressure on the spinal cord caused by DISH. In the meantime, regular aerobic exercise can help you improve your physical endurance and maintain your nimbleness, which can help you cope with DISH.
Symptoms of DISH include pain and stiffness in the spine. Patients may also experience stiffness in the elbows, shoulders, and knees. The pain in these areas can be severe and a doctor may recommend a steroid injection.
Is DISH a form of arthritis?
While Forestier’s disease is commonly associated with osteoarthritis, this condition has a different etiology. It is the result of abnormal calcium buildup in the ligaments and connections between vertebrae. This calcification leads to bone spurs to form along the edges of the vertebrae. The condition typically affects the thoracic and cervical spine.
Another form of the disorder is diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH). This disease affects the lumbar and thoracic spine. It is more common in elderly individuals and in men. It is often diagnosed during unsuspected scans. It often occurs along with osteoarthritis and elevated uric acid levels. As such, it is important to get a diagnosis from a physician.
Diagnosis is based on radiological and clinical features. Both conditions cause back pain, limited range of motion, and stooped posture. However, the clinical symptoms can vary. It is crucial to get a proper diagnosis from your doctor so that you can start treating the condition right away.