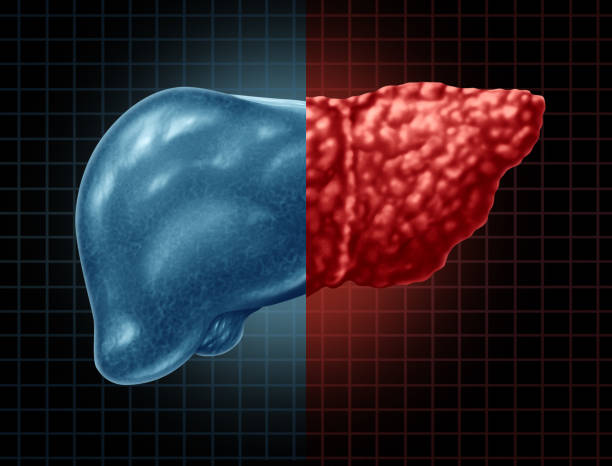
Fatty liver disease is a common health issue, yet most patients do not have any symptoms. While some patients do have fatigue, pain, or discomfort in their abdominal area, the majority do not. Patients may also notice their liver is larger than normal. This disease is not always fatal, but there are ways to treat it.
Can liver fatty be cured?
Although there are no FDA-approved therapies for fatty liver, several companies are developing drugs to treat the disease. These therapies are offered through clinical trials, in which patients are randomized into treatment groups or non-treatment groups. Many companies are also researching other approaches to the disease. If you are suffering from fatty liver, consider enrolling in one of these clinical trials.
The symptoms of fatty liver disease can include cirrhosis, jaundice, itching, and swelling. Though the exact cause of fatty liver disease is unknown, certain health conditions such as alcohol consumption and obesity can make your liver vulnerable to the disease. Treatment for fatty liver disease does not involve surgery, but it can be managed by maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
How serious is a fatty liver?
Fatty liver disease is becoming more common in the Western world, and it has many possible causes. One of these is excessive alcohol consumption over an extended period. Other causes include drug reactions and pregnancy complications. A doctor can confirm a diagnosis by conducting a blood test and imaging tests. A fatty liver biopsy can help determine the severity of the condition.
Early diagnosis is crucial for those at risk for fatty liver disease. While this disease does not cause any noticeable symptoms, it may progress to cirrhosis, which is a more serious condition. This condition causes the liver to enlarge and shrink, and eventually causes scarring. Once the scarring begins, it becomes life-threatening and may require liver transplant.
How do you resolve a fatty liver?
The best treatment for liver disease is a change in lifestyle, which includes avoiding alcohol, losing weight and following a fatty liver diet. However, the exact amount of alcohol you should avoid depends on your specific situation and liver condition. If you are unsure of the amount of alcohol you should avoid, consult a doctor.
A Mediterranean-style diet is best for fatty liver disease. It includes whole grains, extra virgin olive oil, fish and poultry, as well as dairy products like cheese and milk, which are consumed in moderation. However, you should avoid processed foods and added sugars.
What are the symptoms of a fatty liver getting wor
Fatty liver is caused by the buildup of fat in the liver and is a common condition in adults. Overweight and heavy drinkers are at higher risk for developing the condition. People with certain genetic mutations and obesity are also more susceptible to the disease. If you think you have this condition, be sure to visit your doctor as soon as possible.
If the condition is left untreated, it can lead to liver failure, which may lead to other serious health problems. In some cases, fatty liver disease is asymptomatic, but in others, it can lead to the development of severe cirrhosis, which can eventually lead to liver cancer and the need for a liver transplant. People who have cirrhosis are also at greater risk of heart attack and stroke.
Can you live a long life with a fatty liver?
If you’ve recently been diagnosed with fatty liver disease, you may be wondering: can you live a long life with it? There’s no single answer to this question, but the answer can be complicated. A fatty liver is an illness in which the liver becomes scarred and can’t function properly. When this happens, you may have symptoms such as fatigue, confusion, jaundice, and swelling. It can also be a sign of other health problems.
There are different forms of fatty liver disease, and some people are more likely to develop them than others. One type is called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and it affects around 20 percent to 40 percent of the population in the United States. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is most commonly found in people who are overweight and are not drinking alcohol. People with a genetic mutation are also at a higher risk of developing it.