Dyshidrotic Eczema and Autoimmune Disease
If you suffer from dyshidrotic eczema, then you are probably wondering if it is related to autoimmune disease. It can be. Fortunately, there are several treatments for this type of eczema. Read on to learn more about the symptoms, causes, and treatments for this chronic ailment.
Symptoms
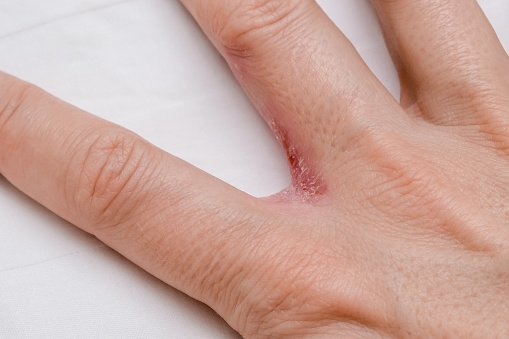
The symptoms of dyshidrotic eczemia include itchy, dry, blistered skin. It may be caused by a number of different things, including an underlying autoimmune disease. This disease can be treated by reducing stress and applying moisturizer to the affected areas. It can also be triggered by certain foods, which may lead to flare-ups of the disease.
The best way to treat dyshidrotic eczema is to avoid triggers. It is important to keep your skin moisturized and to apply topical ointments as directed by your healthcare provider. You can also consider taking oral steroids. Although they are relatively ineffective, they may help control symptoms.
People with dyshidrotic eczema can experience mild to severe symptoms. In mild cases, these symptoms may go away on their own. In other cases, they may be chronic and last for months. If you have persistent symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention.
In some cases, the gene responsible for creating the protective layer on the skin has mutated, leaving the skin more vulnerable to infection. This can cause eczema flare-ups and infection. Other factors may also be at fault. For example, if you live in an area with high levels of pollution or in a climate with low humidity, you are likely to suffer from eczema. Your dermatologist will be able to diagnose you accurately based on your skin’s appearance.
Dyshidrotic eczema and AIHA can be caused by the same autoimmune disease. It causes the immune system to attack healthy cells and mistake them for invaders. In severe cases, your skin can become discolored and you can develop jaundice. Your spleen may even become enlarged.
Treatments
A condition that affects the feet and hands, dyshidrotic eczema is an itchy, chronic skin condition. The symptoms include small blisters on the skin and dry, scaly patches. It is also known as acute palmoplantar eczema, pompholyx, or dyshidrosis. It tends to affect people in their 20s and 30s. People with a weakened immune system may be at an increased risk of developing it.
In severe cases, corticosteroid pills or ointments may be prescribed. However, these can have serious side effects if used for extended periods of time. Some doctors also prescribe immune-suppressing ointments, including tacrolimus and pimecrolimus. While these ointments can be helpful, they may increase the risk of skin infections.
Other treatments for dyshidrotic eczemA include using a moisturizing cream or barrier repair cream. Some dermatologists also prescribe medication that can treat the underlying infection. This medication can be prescribed over a period of several weeks. It should be used according to your healthcare provider’s instructions.
While autoimmune diseases of the skin are not life-threatening, these inflammatory disorders can result in significant emotional consequences and may even lead to permanent disfigurement. The skin is an important barrier between the body and the environment. Severe rashes, however, may be a portal for bacteria to enter the bloodstream.
There are few effective treatments for dyshidrotic eczemA. But there are some over-the-counter treatments that can reduce the symptoms. However, in severe cases, prescription medications may be required. The best way to minimize the effects of dyshidrotic eczema is to keep your skin clean and moisturized.
In severe cases, patients may require the care of a dermatologist. In mild cases, steroid ointments or topical immunosuppressive medications can help with the rash. In severe cases, oral immunosuppressive medications may be prescribed to control the inflammatory process.
Although dietary restrictions can help reduce the symptoms, there are some new therapies that can help patients deal with the condition. A topical calcineurin inhibitor, pimecrolimus, is one example. This medication has shown some long-term efficacy in severe dyshidrotic eczema. However, physicians should exercise caution when using this medication over an extended period of time.
Treatments for refractory eczema
Treatments for dyshidrotic eczemia and autoimmune disease vary widely, and there is no one treatment that can be said to be the best for everyone. In most cases, the condition is idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown. However, there are certain factors that may increase the risk of developing the disease. One of these is high levels of stress. Stress is known to trigger a flare-up of autoimmune conditions.
Using topical steroid creams and ointments can help reduce inflammation and itching. Systemic steroids, such as Etanercept, can also be used to treat the disease. However, they can have undesirable side effects and may even worsen the symptoms.
Aside from the use of topical creams and lotions, patients should also consult their doctors for a diagnosis. An accurate diagnosis is essential. The GP can help diagnose and prescribe the best treatment. It is best to seek treatment as soon as possible. The disease typically affects adults between the ages of twenty and forty, but can occur in anyone. If you’re experiencing a severe outbreak, it’s time to seek medical attention.
Dyshidrotic eczema can be triggered by a number of factors. For example, excessively sweating or wet feet may trigger the condition. During the course of the disease, small fluid-filled blisters can form and cause pain. These blisters tend to last for a few weeks and eventually flake off. In most cases, dyshidrotic eczema affects both hands, but it can also affect the feet.
The underlying cause of eczema is still unknown, but there’s an increasing body of research that suggests that it may be related to an autoimmune disorder. It may be a complication of an autoimmune disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis or type-1 diabetes.
Treatments for dyshidrotic eczma and autoimmune disease are available for people with eczema. The best treatment for this condition aims to limit the occurrence of the symptoms. It involves the use of moisturizers on affected areas every day to help prevent skin dryness. Aside from that, patients should try to reduce the amount of stress that they have in their lives.
Associated with autoimmune disease
Autoimmune disease is a condition that destroys the immune system, and it has been associated with a number of diseases. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People who have a gene variant called auto-antibody have a higher risk of developing autoimmune disease. Autoimmune diseases tend to run in families, and there are certain environmental exposures that trigger their development.
Fortunately, many lifestyle changes may have a beneficial effect on autoimmune disease. For example, adopting a healthy lifestyle may increase a patient’s immunity, which may help them respond better to biologic medications. While no single lifestyle modification can prevent autoimmune disease, a healthy diet and physical activity can improve the overall well-being of patients with autoimmune diseases.
Interestingly, women have a four-fold higher risk of developing autoimmune disease compared to men. Researchers have posited many explanations for this gender difference, but the exact cause is not yet known. One possible explanation is that women have higher levels of circulating antibodies than men, which may influence the pathogenesis of autoimmune disease.
Patients with autoimmune disease may develop autoantibodies many years before they develop clinical disease. This association may be due to an epiphenomenon rather than correlation. In any case, it is important to remember that patients with primary immunodeficiencies may have antibodies against their own immune system. However, it is not clear whether autoantibodies can be correlated with autoimmune disease or not. The researchers suggest that the findings are largely observational and may not be predictive of disease progression.
Although the exact cause of autoimmune diseases remains unclear, the disease is known to be a major contributor to cardiovascular disease and hypertension. Hypertension is often a sign of ongoing inflammation, and many studies have shown that it can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. A large population-based study of RA patients found that hypertension is more common among RA patients than in the general population. Moreover, patients with SLE have a higher risk of hypertension, especially in younger individuals.
The treatment of autoimmune disease often involves immune-suppressants. However, a more natural approach involves identifying the exact causes of the disease and finding the most effective way to address them. Functional medicine is a form of alternative medicine that focuses on treating the underlying cause of the disease. It encourages practitioners to see the body as a holistic system and to learn about each of its systems.