Degenerative disc disease exercises involve slowly bending and stretching your spine while tightening your core. You should hold each position for eight seconds and repeat this process for both sides of your body. This type of exercise can be dangerous and should be done carefully. Never push yourself too far or extend your range of motion beyond what you are comfortable with. If you experience prolonged discomfort, you should stop performing the exercise and consult your doctor.
How do you calm degenerative disc disease?
Exercise can be a great way to help with degenerative disc disease. It helps to reduce pain and build stronger support structures around the disc. It is important to start out slowly and listen to your body’s signals. If you have a lot of pain in your back, you may find it hard to start an exercise routine. However, if you are willing to try new things, exercise can be a great way to calm your degenerative disc disease symptoms.
In addition to exercises, people with degenerative disc disease should also practice good posture to reduce the amount of strain on the spine. Try not to slouch when sitting and make sure to use your legs to lift anything heavy. Also, take pain-relievers or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications to control the pain. You can also try ice or a cold pack. These will help reduce the inflammation around the discs.
A chiropractor in Anchorage can determine whether you have degenerative disc disease. Sometimes, patients may also be experiencing other symptoms, such as a bulging disc. If you are suffering from back pain, your chiropractor in Anchorage will determine if the pain is related to degenerative disc disease or spinal stenosis.
What are the 4 stages of degenerative disc disease
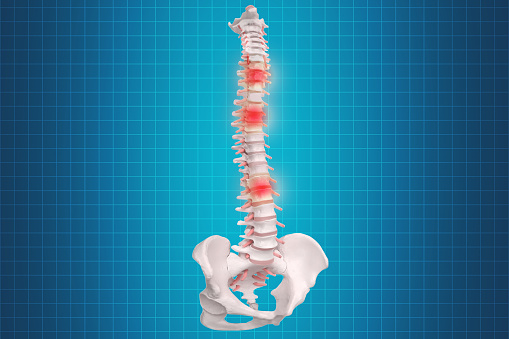
Degenerative disc disease is a progressive condition that affects the discs in the spine. It can lead to painful deformations of the spine and curvature changes. Early diagnosis can improve spinal health and prevent the development of degenerative disc disease. There are four stages of degenerative disc disease, each with unique symptoms.
Stage one involves a gradual loss of disc height and curvature. As the discs wear down, they begin to thin and become narrower. Bony spurs may begin to appear. The pain will become more intense and may impair the patient’s daily activities. People may also exhibit fatigue, sleep disturbances, and altered posture. However, the right treatment can relieve some of the symptoms.
Stage two is the most severe stage. In this stage, the intervertebral disc degenerates and the disc space collapses. A doctor may also notice visible changes in the vertebrae surrounding the affected disc. Pressure on the spinal cord from the herniated disc can cause pain and neurological symptoms. Depending on the location of the herniation, symptoms may vary.
What is L4 L5 degenerative disc disease?
L4-L5 degenerative disc disease can be one of the leading causes of low back pain. This condition can become worse as time goes on, especially when the patient continues to exert stress on the spine. This condition is characterized by a rupture of the inner nucleus pulposus, which is located at the L4-L5 vertebrae. The fragments of the disc material press against the nerve roots located behind the disc space, causing pain and weakness. Herniated discs are most common at the L4-5 and L5-S1 levels.
The symptoms of L4-L5 degenerative disc disease include periods of intense pain that may last a few days or months. The pain can range from mild to excruciating, and it can affect your lower back, buttocks, neck, and arms. Some people also experience numbness or tingling in their extremities. Other symptoms include weakness in the leg muscles. In severe cases, the patient may experience foot drop.
If your L4-L5 disc bulge is a symptom of L4-L5 degenerative disc disease, you should seek immediate medical attention. Your physician may try to fix the disc or spinal joints using non-surgical techniques. However, this procedure is not always effective in the long term, and patients often return for additional surgeries.
Why does a person get degenerative disc disease?
Degenerative disc disease is a common problem affecting the spine. The condition can cause many symptoms, including back pain and instability of the limbs. A professional diagnosis is necessary to find the best treatment for your pain. A doctor will evaluate your back pain and medical history and develop a treatment plan based on your individual symptoms. Treatments can include non-surgical procedures or medications.
The symptoms of degenerative disc disease can vary from person to person. However, some patients may experience numbness, tingling, muscle weakness, and a lack of flexibility in their legs. A doctor will look for these symptoms and may prescribe over-the-counter pain medications or prescription medications. They may also prescribe muscle relaxants to relieve painful muscle spasms. If the condition continues, the doctor may perform X-rays to determine the cause of your pain.
Degenerative disc disease occurs when discs break down and lose their water content. This happens over a period of time due to years of use. As a result, a cracked or fissured disc can put pressure on the spinal nerves, which may lead to pain and numbness.
How long can you go with degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease can be difficult to treat and sometimes even painful, but exercises can help the condition heal faster. A physical therapist can teach you how to lift objects properly and stretch the muscles of your back, legs and stomach. These exercises can also help you keep your spine flexible. Your doctor may also prescribe over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications to control pain and inflammation. Your physical therapist can also recommend a back brace for added support.
Another form of exercise can be spinal decompression. This involves hanging over a swiss ball. This exercise gives the discs room to expand and fill with fluid, which will prevent degeneration-related pain. This exercise is particularly useful if you have degenerative disc disease in your neck.
When you have degenerative disc disease, you should try to stay active as much as possible. The shortened space between discs causes pain, which is exacerbated by sitting. You should also avoid bending or twisting your back, which can further aggravate your condition. Exercises such as walking, running, or swimming can help you feel better. However, if you have been diagnosed in your twenties, you may be wondering whether you’ll continue to experience pain and stiffness when you get older. You should know that age can also cause degenerative disc disease, but there are things you can do to keep it under control.
What is L5 S1 degenerative disc disease?
L5-S1 degenerative disc disease causes pain in the L5-S1 area. It can start suddenly after an injury or develop over time. It is often worsened by prolonged sitting, standing, or bending. The pain is usually sharp and can radiate to the skin. It can affect one or both legs and affect a person’s ability to walk.
In this case study, a patient is presented with an L5-S1 disc problem that has progressed since she underwent back surgery for a previous disc herniation. She complains of low back pain that extends down her buttocks and radiates down the posterolateral and posterior thighs. Earlier, she underwent L5-S1 recurrent disc excision and experienced excellent pain relief. However, she is now experiencing back pain that has returned. Her back pain has made her unable to lift her legs.
Degeneration in the L5-S1 disc is caused by degeneration of the annulus. In this condition, the nucleus pushes out the annular fibers, causing a disc herniation, extrusion, or sequestration. As a result, the degenerated disc begins to collapse. The disease is called spondylolisthesis and has many associated symptoms. The condition can be congenital or developmental.
What are the symptoms of L4-L5 nerve damage?
There are many symptoms associated with a damaged L4-L5 nerve. One of the most common symptoms is pain in the front of the leg or the thigh. Another symptom is weakness in the quadriceps muscle. These symptoms may radiate to the front of the shin, back of the thigh, or the front of the foot.
Nerve damage can also result in numbness or tingling in the foot or leg. These symptoms can occur on either side of the L4-L5 nerve. Some people have no symptoms at all, while others may experience numbness or tingling. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to seek treatment as soon as possible. There are several types of treatments available.
There are many causes of L4-L5 nerve damage. The most common cause is a bone spur, but it can also be caused by degenerative changes in the bone. Another cause is external trauma such as a fracture or facet joint dislocation. Other causes include infections and tumors of the L4-L5 vertebrae. In some cases, nerve damage in the L4-L5 vertebra causes referred pain in the back, thighs, or lower back.
What can be done for L5-S1 degenerative disc?
One of the best ways to address degenerative disc disease is through regular exercise. However, it is important to start slowly and listen to your body. In addition to being good for your overall health, aerobic exercise can also help prevent flare-ups of degenerative disc disease and decrease pain during flare-ups. Try stationary biking or elliptical training. These activities are both low-impact and easy on the lower back.
Stretching exercises may help you ease pain by extending your hamstrings. You can also perform flexion and extension exercises while standing, which help strengthen the back muscles. Weight resistance training can also be helpful. Performing basic sit-ups can also help treat back problems associated with disc herniation.
Depending on the severity of your degenerative disc disease, your doctor may recommend surgery to relieve pressure on your spinal nerves and discs. While most patients won’t require surgery, some people may benefit from it if their condition is severe enough to cause pain or weakness. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove bone spurs or expand the opening to the nerve roots. In other cases, surgery may be necessary to connect two or more vertebrae to relieve the pressure on the nerves. Exercise is also an excellent alternative to surgery for many patients.