Crohn’s Disease Symptoms in Females and Pregnancy
If you have Crohn’s disease (CD) and you’re a female, you may be wondering if the symptoms are related to pregnancy. Fortunately, CD symptoms in women are often similar to those in non-pregnant women, and most treatments have been proven safe during pregnancy. If you have CD and you’re planning on getting pregnant, you’ll want to find a doctor early so you can be fully informed about your condition.
What foods trigger Crohn’s disease?
Depending on the cause, consuming high-fat foods such as butter and margarine may exacerbate Crohn’s symptoms. The same holds true for other food groups such as fatty meat and deep-fried food. In such cases, it’s best to limit these foods in your diet and replace them with lean proteins. Also, limit the amount of dairy you consume.
Smoking and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may increase your risk for developing Crohn’s disease. These drugs can contribute to the inflammation of the bowel and aggravate the symptoms of Crohn’s.
What do Crohn’s pains feel like?
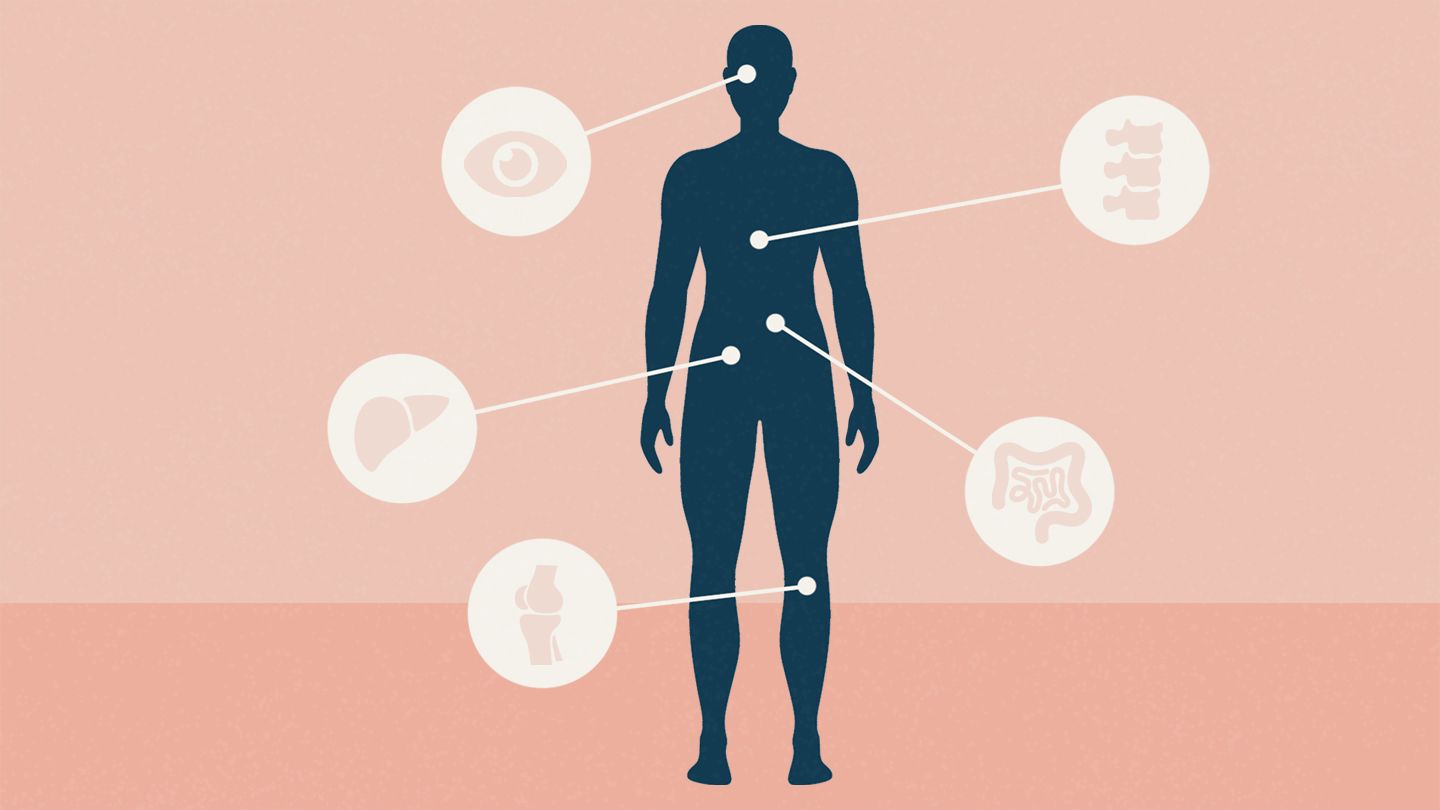
Crohn’s disease symptoms in females vary depending on the type of disease and the severity of symptoms. Some symptoms include weight gain or loss, heavy periods or no periods, and sometimes even fertility problems. Some symptoms can be managed and may disappear completely when the disease enters remission.
Inflammation of the GI tract is one of the most common symptoms of Crohn’s disease. These symptoms can occur anywhere in the digestive tract and can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. Crohn’s disease can also cause scarring of the lining of the intestinal tract, which can lead to painful obstructions. Other painful symptoms include ulcers and abscesses. Crohn’s disease can also cause pain and bleeding during bowel movements.
Crohn’s disease symptoms can also be exacerbated by certain factors, such as stress and certain foods. A doctor can make a definitive diagnosis of the condition with diagnostic imaging tests. These tests include an upper GI series, which uses a special liquid called barium to make the upper GI tract visible on x-ray.
How do you test for Crohn’s?
To diagnose Crohn’s disease, the first step is to conduct a physical exam. Your doctor will ask you about your overall health, diet, family history, and daily activities. They may also perform diagnostic testing to rule out any other underlying conditions. This could include laboratory tests and X-rays of your gastrointestinal tract. Depending on the type of Crohn’s disease you have, a GI tract examination may include the addition of a contrast chemical to improve images.
In addition to gastrointestinal symptoms, Crohn’s disease in females can manifest as extraintestinal or systemic symptoms. About 36 percent of patients have extraintestinal symptoms, which can include swollen joints and a painful lower back. In addition, the disease can cause rashes and bumps on the skin and eyes. Some women also experience night sweats or fatigue and their menstrual cycle can become irregular.
Does Crohn’s cause big belly?
A new study has uncovered a possible link between Crohn’s disease and a large belly in females. Adipose tissue is an important part of the endocrine system in the human body, which produces chemical signals and proteins in the body. These hormones are involved in many bodily functions, including regulating the immune system and intestinal cells. However, it is still unclear if Crohn’s disease is the only cause of a big belly in females.
Crohn’s disease is a complex chronic disorder affecting the digestive system. The most common areas affected are the lower part of the small intestine and the beginning of the large intestine. However, it may affect any part of the digestive system. Symptoms can include abdominal pain and loss of appetite. Patients may also experience diarrhea or watery stools. Physical examination may also reveal a mass in the abdomen. The condition may also affect the joints, skin, and eyes.