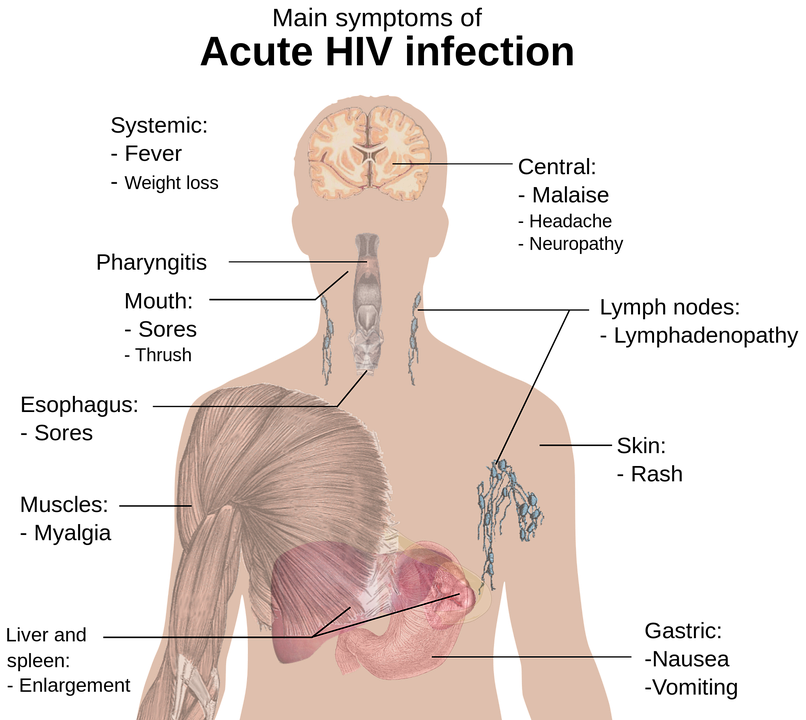
Crabs disease is an STD which is caused by a crab infestation. If you’re thinking of having a crab infestation, you should know what to look out for and the symptoms of crabs disease. You should also know that it’s not contagious and it can be treated without a doctor’s prescription.
How do you get crabs disease?
Crabs are commonly found in the pubic region, but they can also be found on clothing, eyelashes, and beards and mustaches. Often, a person can get infected by rubbing their skin on infested surfaces. The disease can also be passed to humans through sexual intercourse. If you are infected, you should wash all of your clothing, bedding, and towels in hot water. Crabs are not very persistent, and they usually do not stay near your body for long. However, if you do find them, you should see a doctor as soon as possible. The doctor may recommend that you use a medicine-based shampoo to kill crabs. You can also apply lotion to the pubic area.
Treatment for crabs may cause itching. Using hydrocortisone cream may help with the discomfort. Most of the nits will remain attached to the hair, but a fine-tooth comb may be used to remove them. You should also wear clean clothing after treatment, and you should sleep on bed linens that are freshly laundered. Also, if you have sex partners, you should tell them about the infection, and abstain from having sex until the crabs are removed.
Is crabs a real STD?
While it may be difficult to tell your partner that you have an STD, it is important to do so. It will help you get treatment and avoid contracting the disease. In the event that you are infected, you should avoid close contact with other people and wash all of your bedding and clothing in hot water. In the event that you cannot wash your clothes, you should dry clean them. In addition, it is important to get your partner checked regularly. If your partner has an STD, you should not have sexual activity with them until they have been treated.
Most cases of crabs occur during intimate contact. This is because crabs can attach to pubic hair on human bodies and then move from one person to the next. Unlike other sexually transmitted diseases, crabs do not require sexual penetration in order to spread. Crabs can live for up to 24 hours off a human body. Although they can cause itchiness and other symptoms, they are generally harmless.
What are the symptoms of crabs disease?
If you suspect you have been bitten by a crab, you should see a doctor. They can check the area with a microscope to make sure there are no other causes of your itching. Depending on the location of the bite, you may find a dark blue mark on your skin. Crab bites are most common when a person has been exposed to pubic lice. People with coarse hair are also at risk of getting bitten by a crab.
Crabs are tiny brownish-red or grey insects that live primarily in the pubic hair, but can also live in eyelashes, eyebrows, armpits, and facial hair. Crabs can be spread by sexual contact, but it is uncommon for a human to contract crabs through the toilet seat. Crabs live for a few days off the human body, and an allergic reaction to the crabs’ saliva can cause intense itching.
Can crabs be cured?
Crabs are generally harmless but you should visit a doctor if you notice the signs of an infestation. A doctor can prescribe a hydrocortisone cream that can stop the itching. Afterward, you should wash all your bedding and clothes. It is best to wash the clothing and bedding on hot and dry cycle. If you cannot wash them, you can try to dry clean them. However, you should not use the same bed linens for the next two weeks. It’s also important to notify your sexual partner so that they can get treated. During this time, you should avoid having sex with them until the infection is treated.
Pubic lice are small parasitic insects that feed on human blood. These critters live in pubic hair (the hair around the front of the genital area) and other parts of the body with coarse hair. Millions of people suffer from pubic lice every year. These tiny creatures don’t live long once they fall off the body.