How to Take a Celiac Disease Quiz
Celiac disease is a type of food allergy and rarely affects people who are not of European ancestry. Though the condition can be painful, it is not life threatening and can be treated by following a gluten-free diet. It is important to know that it is not uncommon to eat a little gluten. In fact, many people with the disease are able to eat some gluten without any negative effects.
Can I test myself for celiac disease?
At-home tests are now available that can detect a person’s risk for celiac disease without a visit to the doctor. These tests require a small blood sample and do not require an appointment or travel time. They provide initial information about celiac disease, which can help you initiate a conversation with a health care provider. The cost of these tests is typically not covered by health insurance.
While it is advisable to seek medical attention if you suspect you may have the disease, you should be aware that it runs in families. People who have first degree relatives with the disease are at greater risk of developing the condition. People with certain genetic disorders may also have symptoms.
The most common test for celiac disease is an immunoglobulin A test, which tests the amount of immunoglobulin A in the blood. The test is highly sensitive, and it can detect high levels of antibody. However, it is not a reliable test for early diagnosis of celiac disease. The test will not be positive until the disease has already caused extensive damage to the small intestine.
What can be mistaken as celiac disease?
It’s possible for symptoms of celiac disease to be confused with other illnesses. The symptoms of celiac disease can be similar to those of Crohn’s disease, diverticulitis, irritable bowel syndrome, and dermatological problems. Doctors can confirm a diagnosis of celiac disease with blood tests and intestinal biopsies.
Diagnosing celiac disease can be difficult and time-consuming, and it’s important to get the right diagnosis. However, because the symptoms of celiac disease can mimic other conditions, diagnosis is often delayed for months or years. This is why many people have to visit multiple physicians before a diagnosis is made.
If you have celiac disease, you’ll have to avoid gluten to prevent it from damaging your small intestine. Gluten causes the immune system to attack the small intestine, leading to an array of health problems.
Can you go undiagnosed with celiac disease?
A typical celiac disease diagnosis begins with a blood test that looks for elevated levels of specific antibodies. These antibodies indicate a person has celiac disease. However, elevated antibody levels may also indicate other diseases such as lactose intolerance, Crohn’s disease, or bacterial overgrowth. Occasionally, a patient will undergo a bowel biopsy to confirm their diagnosis.
Symptoms of celiac disease can include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Those with the disease can also experience non-gastrointestinal symptoms, including dermatitis herpetiformis, delayed puberty, and recurrent headaches. In some cases, patients may also suffer from bone pain and achy joints.
Although celiac disease is generally associated with digestive problems, some people do not display any symptoms at all. While the disease generally presents with abdominal pain, some sufferers may also experience other symptoms such as anemia, bones disease, migraines, and reproductive problems. Symptoms may vary depending on age and severity. Sometimes, people may not experience any symptoms at all or may not experience any until after they go on a gluten-free diet.
Can you all of a sudden be celiac?
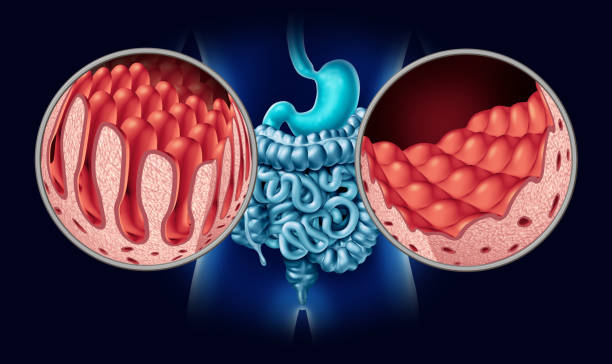
Celiac disease is a gastrointestinal disorder that can be triggered by gluten ingestion. The body interprets gluten as an invader and starts to produce antibodies that attack the villi, the small intestine’s lining. This inflammation damages the villi and leads to the development of the disease.
Although the exact cause of celiac disease is unknown, many factors contribute to its development. Genetics and infant feeding practices may be involved, as are gastrointestinal infections and gut bacteria. It can also be triggered by severe emotional stress or by surgery. In any case, celiac disease affects the small intestine and damages the villi, which shrivel up and stop functioning properly.
If you think you might have the disease, you should visit your doctor. Diagnosing it can be difficult, as the symptoms can be similar to other conditions. Your doctor will most likely order a screening blood test to see if you’re affected by the condition.
What does undiagnosed celiac feel like?
There are many symptoms of celiac disease, including bloating, gas, and abdominal pain. However, up to 60% of people with the disorder do not display any symptoms. This lack of symptoms is a big reason why celiac patients go undiagnosed. The absence of gastrointestinal symptoms is also a big cause of misdiagnosis. Recent research from the University of Sheffield has also found that people with celiac disease may have damage to the brain.
The symptoms of celiac disease can vary between individuals, ranging from mild to severe. In some cases, the condition can be characterized by abdominal pain and diarrhea. In other cases, a person may experience moodiness or depression or experience skin rashes. While there is no single symptom of the disease, it’s important to get diagnosed early to prevent severe complications.
A person suffering from undiagnosed celiac disease may experience chronic diarrhea, fatigue, or anemia. In addition, the condition can affect the bones, the brain, and the reproductive system. Although these symptoms are common, undiagnosed celiac disease can have other, less obvious symptoms.
Where is celiac pain located?
When someone eats a product containing gluten, they often experience pain in the stomach. This pain can be dull or sharp, or it can be accompanied by spasms or cramping. In some cases, people may also have pain in other parts of the body. In these cases, a trip to the doctor may be necessary to find a solution to the problem.
A doctor may perform blood tests to determine the amount of gluten in your blood, as well as check antibodies to gluten. Those antibodies may indicate the presence of celiac disease. He or she may also perform an upper endoscopy, which looks inside your small intestine to look for damage to the villi. This procedure is generally done under anesthesia or sedation.
Other symptoms of celiac disease may include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating. In some people, the disease will also cause symptoms such as infertility, depression, or irritability. A few people may have no symptoms at all.
What is a gluten belly?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the body is unable to absorb the essential nutrients in food due to damage to the villi, which line the small intestine. Because of this damage, the villi cannot absorb vitamins and nutrients necessary for proper growth and development. This condition is usually inherited but can also develop as a complication of other disorders.
Despite the fact that cutting out gluten is the first step for treating celiac disease, up to 20% of sufferers still suffer from symptoms. They may also have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which is a condition that affects the large intestine. People with IBS may experience diarrhea, bloating, and strong stomach pains. They may also have mucus in their stool.
A blood test is another way to diagnose celiac disease. It checks the amount of infection-fighting cells in the blood and antibodies to gluten (a protein found in foods). Another test involves getting a tissue sample from the small intestine to check for damage to the villi. This is usually done by passing a thin tube through the mouth or stomach. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What does a gluten stomach ache feel like?
Gluten intolerance is common, but you don’t have to have it to experience stomach aches after eating gluten-containing foods. You just need to pay attention to your body’s signs and symptoms. One sign is bloating, which happens when your stomach feels full of gas or swells after eating gluten. This is often due to overeating, but it can also be a sign of gluten intolerance.
If you think you might be suffering from Celiac disease or gluten sensitivity, there are several steps you can take to heal your gut and prevent stomach aches from recurring. You can start by keeping a detailed food journal. This will help you identify the foods that trigger your bloating.
The symptoms of coeliac disease vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe. They are often hard to diagnose and may be similar to those of wheat intolerance or irritable bowel syndrome. Some people with Celiac disease can experience abdominal pain, diarrhoea, bloating and lethargy after eating gluten.