The long-term effects of autoimmune disease in cats are not well understood. The disease can be either asymptomatic or fatal. Nevertheless, if you think that your cat is suffering from autoimmune disease, see your veterinarian. You can find out more about this condition and its causes by reading the articles in this article.
How long does a cat live with autoimmune disease?
The prognosis of autoimmune disease in cats is based on how severe the condition is and how long it takes to treat it. It is usually a progressive condition that requires a number of tests and treatments to manage. Although it can be life threatening, it is usually treatable with the proper medication.
The disease is associated with an overactive immune system, which forms antibodies to its own tissues and attacks healthy cells. Traditional veterinary treatment typically involves steroids and blood transfusions. Ultimately, the most important thing to do to treat autoimmune disease in cats and dogs is to modulate the immune system.
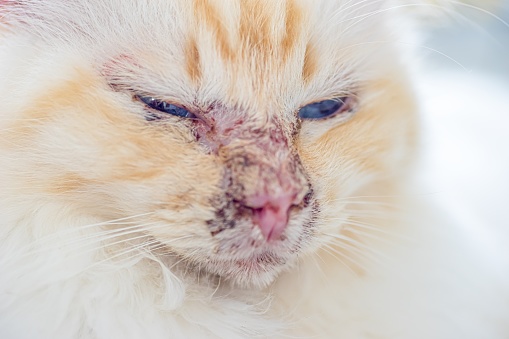
Pemphigus foliaceus is one of the most common autoimmune diseases in cats. It begins with itchy skin and leads to blisters and ulcers. The ulcers may develop in the groin, armpit, or mouth. Vesiculites may develop as well. These lesions can rupture, and the cat may need hospitalization to receive biopsies. In some cases, the disease resolves spontaneously.
Is autoimmune disease curable in cats?
Autoimmune diseases in cats are a difficult condition to diagnose and are rare. They result when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, organs, or tissues. These diseases are similar to human autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and lupus. Their cause is unclear, but medical researchers believe that diet, infections, and exposure to certain chemicals can contribute to the development of these diseases.
Although the exact cause of PF remains a mystery, several treatments are available. One of the most commonly used drugs is chlorambucil, which is given to cats with PF as a monotherapy. However, the drug is not without side effects, and a platelet count must be performed before prescribing chlorambucil. Another option is gold salts, which have immunomodulating and anti-inflammatory effects. Cyclosporine, a nonsteroidal immunosuppressive medication, is another treatment option. However, its use is associated with a risk of side effects that may include vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, weight loss, and gingival hyperplasia.
In addition to these treatments, a biopsy is required to diagnose autoimmune skin disease in cats. The biopsy may be done using local anesthetic or may require general anesthesia. The biopsy involves removing a small round patch of skin from the affected area. This sample is then sent to a veterinary pathologist for testing.
What happens when a cat has an autoimmune disease?
If your cat has an autoimmune disease, you will want to make sure you take the best care of him. Your veterinarian can give you some options to treat your cat. If your cat has an autoimmune disease, he will likely need immunosuppression to control the immune system. Some of these diseases are not curable, but they can be treated successfully. The treatment you choose will depend on the cause and your cat’s symptoms.
Autoimmune diseases are a complex group of diseases in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues. A human example is type 1 diabetes. These diseases are often complicated to diagnose in animals because they affect so many different body systems. Some of these diseases are life-threatening and can be difficult to treat.
One of the most common autoimmune diseases in cats is hyperthyroidism. A cat with hyperthyroidism produces too much thyroid hormone. This can have negative effects on their heart, nervous system, and digestive system. In addition, hyperthyroidism in cats can cause weight loss, restlessness, poor hair coat, and rapid breathing. In addition, autoimmune diseases in cats are often a symptom of a cat’s underlying autoimmune disease.
Can autoimmune disease be fixed?
While the long-term prognosis of lupus in cats is still unclear, it is generally known that it requires extensive medical treatment. Treatment options for this life-threatening condition include immunosuppression with corticosteroid drugs, a special diet, and standard vaccinations. In some cases, the disease may be curable, but it is important to identify it early.
Symptoms of autoimmune disease in cats are not always easy to recognize. They may be confused with other diseases, but most affected cats will have skin lesions. These lesions can be ulcers, sores, or redness, and can occur anywhere on the body. To properly diagnose this condition, a veterinarian will perform a series of tests to determine the exact cause. These tests can include a complete physical exam, skin biopsies, and an antinuclear antibody test.
One type of autoimmune disease in cats is pemphigus foliaceus, which causes itchy, crusty skin. It usually starts with ulcers in the groin, arms, and mouth, and may eventually progress to blisters. These lesions may rupture and require medical attention and treatment.
How do vets test for autoimmune disease?
A veterinarian can test for autoimmune disease in cats by performing a number of tests. These tests can be misleading, however. The most common symptom of autoimmune disease in cats is skin lesions, which usually appear on the paws, face, or ears. If your cat is showing symptoms, you should see a veterinarian as soon as possible to ensure that the condition is not worsening. Your vet may also prescribe a special diet to control the disease and make your cat as comfortable as possible.
If the disease is affecting the skin, a biopsy may be required. This procedure may be performed under local anesthetic or with general anesthesia. During this procedure, a small round block of skin is removed from the affected area and sent to a veterinary pathologist for diagnosis.
Another test your veterinarian may use is a general blood profile. This test will take a look at your cat’s red and white blood cells and biochemistry, and can reveal organ damage. However, no single test is 100 percent accurate, and false results may occur in cases of liver disease or feline leukemia. Therefore, your vet may also harvest blood samples from specific areas of your cat’s body in order to confirm the diagnosis.
What causes autoimmune disease?
Symptoms of autoimmune disease in cats are often vague, but they can include anemia, weight loss, and lack of energy. If you’re unsure about a symptom, ask your veterinarian. In severe cases, a biopsy may be necessary. This involves removing a small round block of skin for diagnosis.
Autoimmune disease in cats is caused by a cat’s own immune system attacking its own cells. While the body normally defends itself against foreign bacteria and viruses, an autoimmune disease causes the immune system to attack the cat’s own cells. It can affect different cells and multiple organs.
The cause of autoimmune disease in cats may be a combination of factors. One of the most common factors is poor digestion. Poor digestion can lead to inflammation, which taxes the immune system. Food allergens may also contribute to the inflammation. Unfortunately, many pet owners don’t realize that many foods can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases. Most dry food contains a high amount of starchy carbohydrates, which are converted to sugar by the body.
What vitamin is good for autoimmune diseases?
There are a few supplements available that may help your cat with autoimmune diseases. Fatty acids, in particular omega-3 fatty acids, may help regulate the immune system. Many holistic veterinarians also recommend anti-inflammatory agents. However, there are no controlled studies to prove that these products are effective in treating autoimmune diseases in cats.
The best way to keep your cat’s immune system healthy is to feed it a balanced diet rich in natural, biologically appropriate nutrients. Vitamin C is especially important, as are nutrients such as zinc. In addition to these, immune support supplements may also help pets with autoimmune diseases. A weak or overactive immune system can lead to allergies, chronic infections, and even cancer.
What can trigger autoimmune flare?
Autoimmune diseases in cats can cause a range of symptoms and are hard to diagnose. These diseases are caused by the body’s immune system attacking healthy cells, tissues, and organs. They are similar to rheumatoid arthritis, type 1 diabetes, and celiac disease. The cause is unknown, but medical researchers believe that diet, infections, and exposure to chemicals may be factors.
Symptoms vary from person to person and may include skin lesions, joint swelling, and gastrointestinal problems. A thorough diagnosis and treatment is necessary, and it is important to know what’s causing the symptoms. While autoimmune disease can be life-threatening, it can usually be controlled with medication.
The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but genetic predisposition may be a risk factor. Certain environmental factors, like ultraviolet light, can lead to lupus flares. Most common types of affected cats include Persian, Siamese, and Himalayan cats. Since symptoms of lupus are similar to those of other conditions, it’s crucial to see a veterinarian for a proper diagnosis.