Symptoms of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
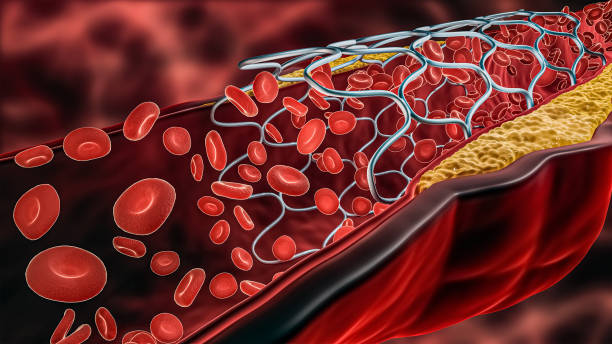
Symptoms of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease can range from mild to severe. Some people with atherosclerosis may be asymptomatic for decades. Symptoms may only emerge when plaques become so large that they block blood flow. When a lesion reduces the arterial lumen by more than 70%, a person will experience transient ischemic symptoms. When atherosclerosis reaches the arterial wall, it can also lead to arterial dissection or aneurysms. Other symptoms may include pain, swelling, an abnormal pulsation, or sudden death.
What are the warning signs of atherosclerosis?
If you are over 65 and have a family history of heart disease, you may be at risk for atherosclerosis. This condition occurs when fatty deposits build up in the artery walls. As a result, the arteries narrow and cannot provide proper blood flow.
The warning signs of atherosclerosis include elevated blood cholesterol levels, high blood pressure, and an increased risk of heart attacks. However, some people do not show any of the classic risk factors. In these cases, a doctor will perform certain tests to determine whether you are at risk of atherosclerosis. These include a blood test for cholesterol and blood pressure, a stress test, and an electrocardiogram. These tests can detect abnormalities in heart rhythms and blood pressure levels and also detect blockages.
Although the signs of atherosclerosis may vary depending on which arteries are affected, you should seek medical attention immediately. Affected arteries can cause numbness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and leg pain.
What are the 4 stages of atherosclerosis?
The development of atherosclerosis involves changes in the artery’s wall. These changes can’t be seen with the naked eye, but they build up over time and result in major damage. The process begins with damage to the inner layer of the artery’s wall, called the intima. This inner layer is lined with endothelial cells, which act as barriers between the blood and the artery’s wall.
The endothelium contains cells called mononuclear leukocytes. These cells have two functions, one contractile and one synthetic. They release a substance called vasoactive substances, which control blood flow. The endothelium also contains a layer of tissue known as lamina elastica, which regulates the elasticity of vessels. When the lamina elastica weakens, the blood can’t flow properly through it, and clots can form in the blood. If this blockage continues, it can result in aneurysm, a serious complication of atherosclerosis.
Is atherosclerosis a serious heart disease?
If you’re concerned about the blockage of your coronary arteries, you may want to learn more about the symptoms of atherosclerosis. It’s a common condition that can cause a variety of symptoms, including shortness of breath, fatigue, and even insomnia. If you think that you have the condition, you should see a doctor immediately. However, some people may not experience any symptoms at all.
Treatments for atherosclerosis focus on reducing the risk of a heart attack or stroke. They may also target specific risk factors and help to prevent blood clots and plaque buildup. Lifestyle changes, including quitting smoking and maintaining a healthy weight, may also help patients cope with the symptoms.
What is the best treatment for atherosclerosis?
Treatment for atherosclerosis varies depending on your condition. If it’s severe, your cardiologist may recommend surgery. If it’s less severe, lifestyle changes can help you manage the condition. Your healthcare provider can also prescribe medicines that prevent the buildup of plaque.
While there’s no specific cure for atherosclerosis, a healthy lifestyle and regular medical care can prevent it and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke. Although atherosclerosis is often difficult to treat, proper management of the disease can greatly improve your quality of life. For starters, you should quit smoking, which increases the risk of plaque buildup in your arteries.
There are several types of medications to treat atherosclerosis. Some of these medications help lower cholesterol and control blood sugar. Other medications help prevent blood clots. Some treatments include lifestyle changes and medications to control other medical conditions, such as diabetes.
What is atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a condition characterized by hardened and narrowed arteries. As a result, the arteries cannot deliver adequate blood and oxygen to the body. This can lead to tissue death and infection. If left untreated, plaque may break free and cause damage to the arteries. The condition can also result in blood clots. The onset of atherosclerosis may be early in life, or it may develop gradually over time.
When plaque forms on the inner wall of the artery, it begins to form a film. This film is made up of cholesterol and fatty substances. It also contains calcium and cellular waste products. This buildup causes inflammation and thickens the artery walls, reducing the flow of blood and oxygen to vital organs.